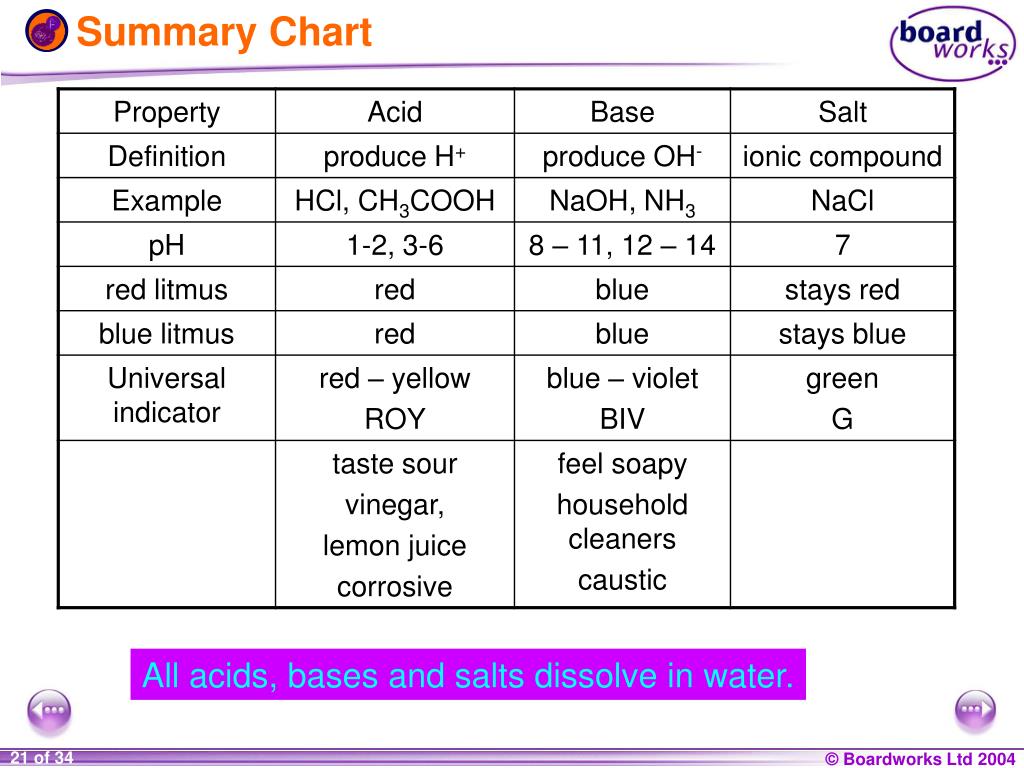
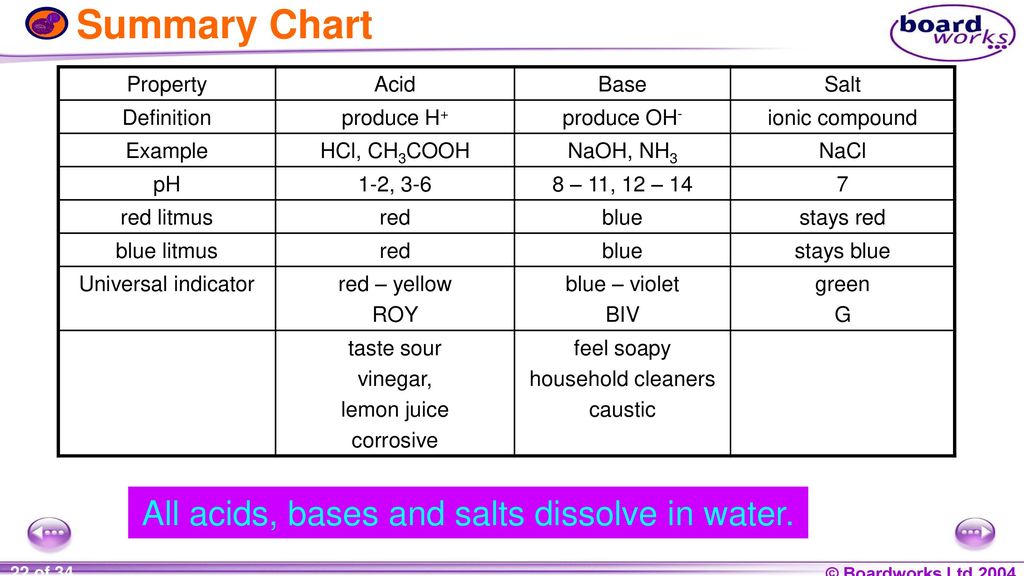
Acids And Base Chart

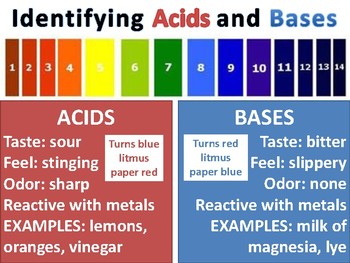
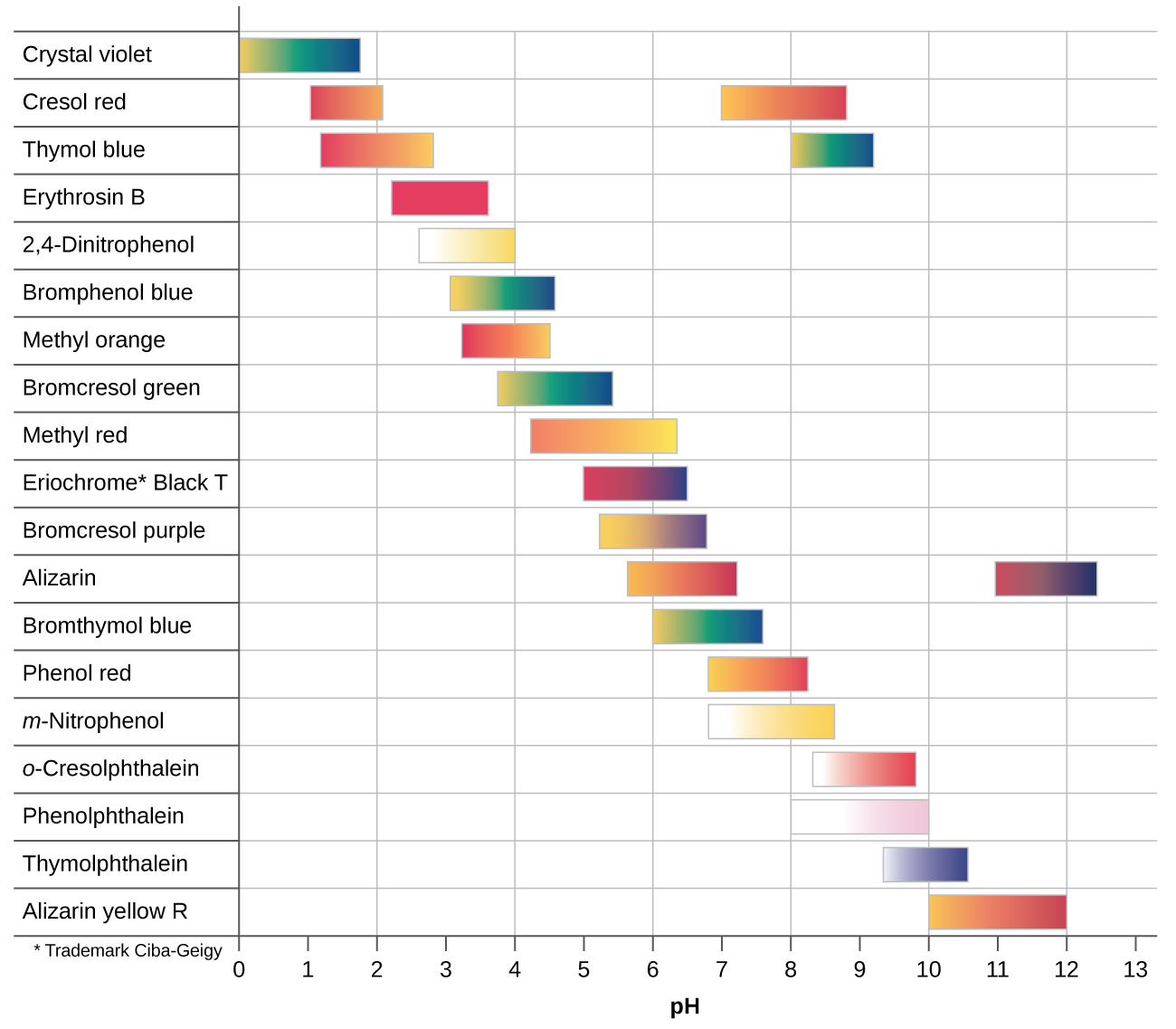
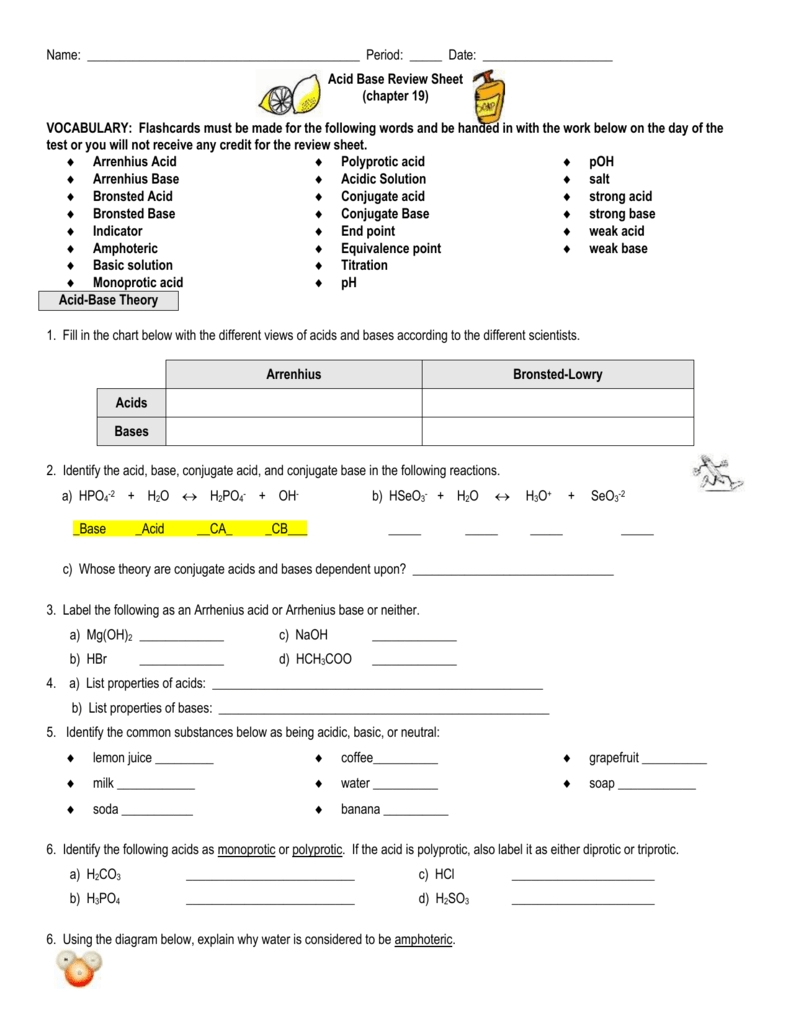
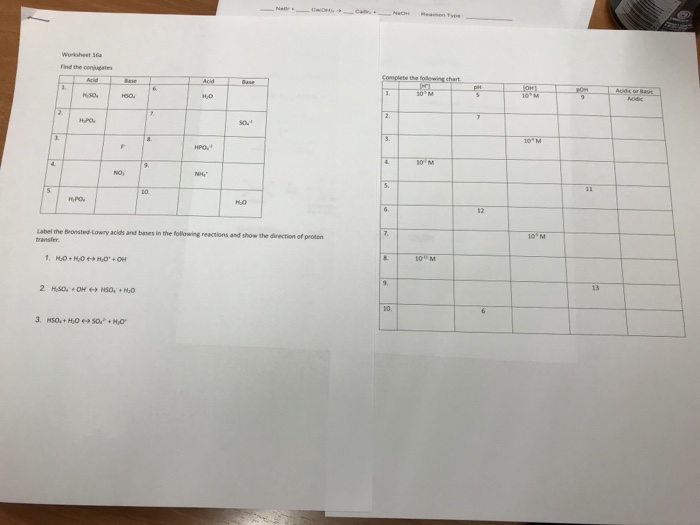
An acid base indicator is a weak acid or a weak base.
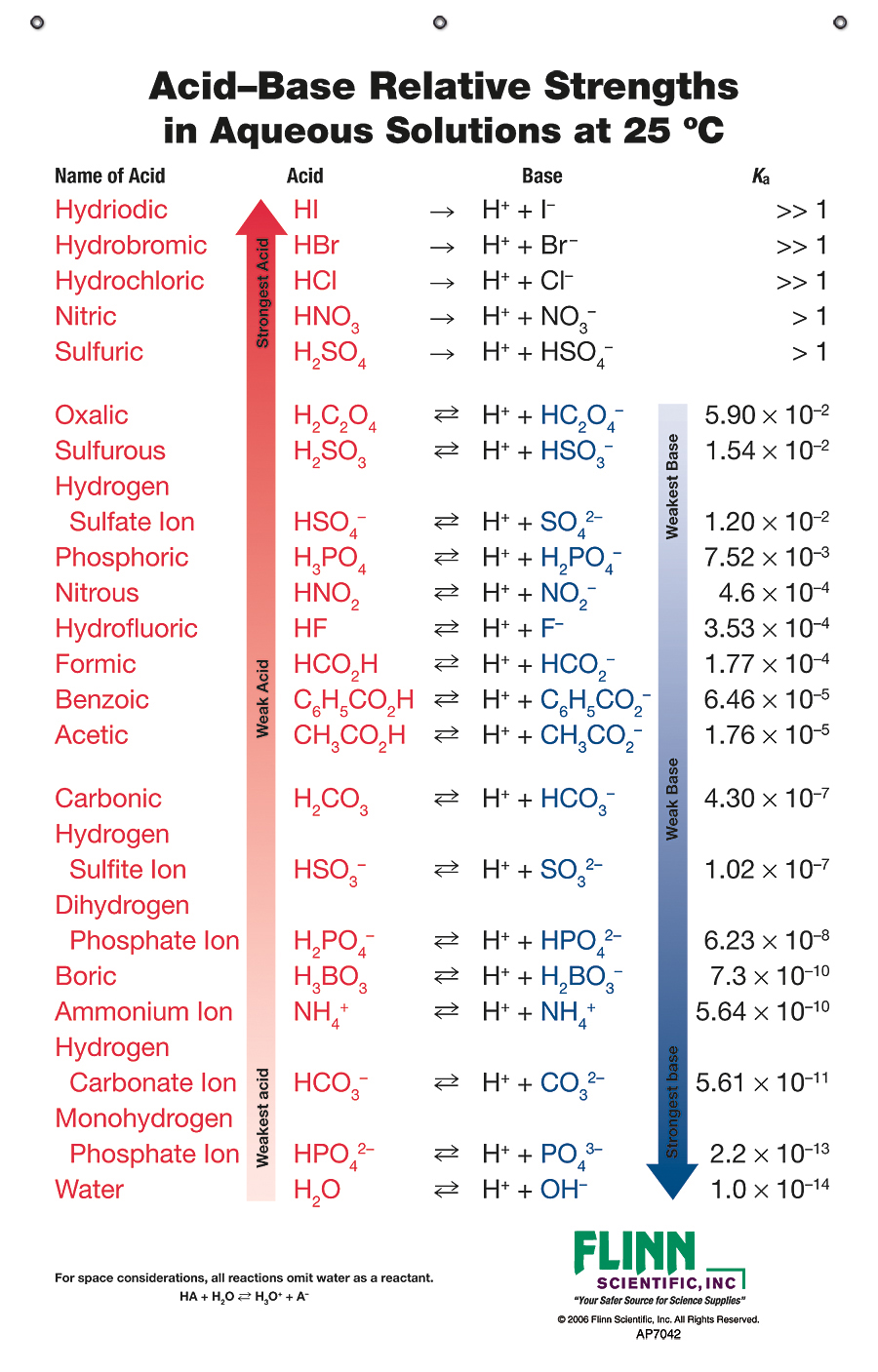
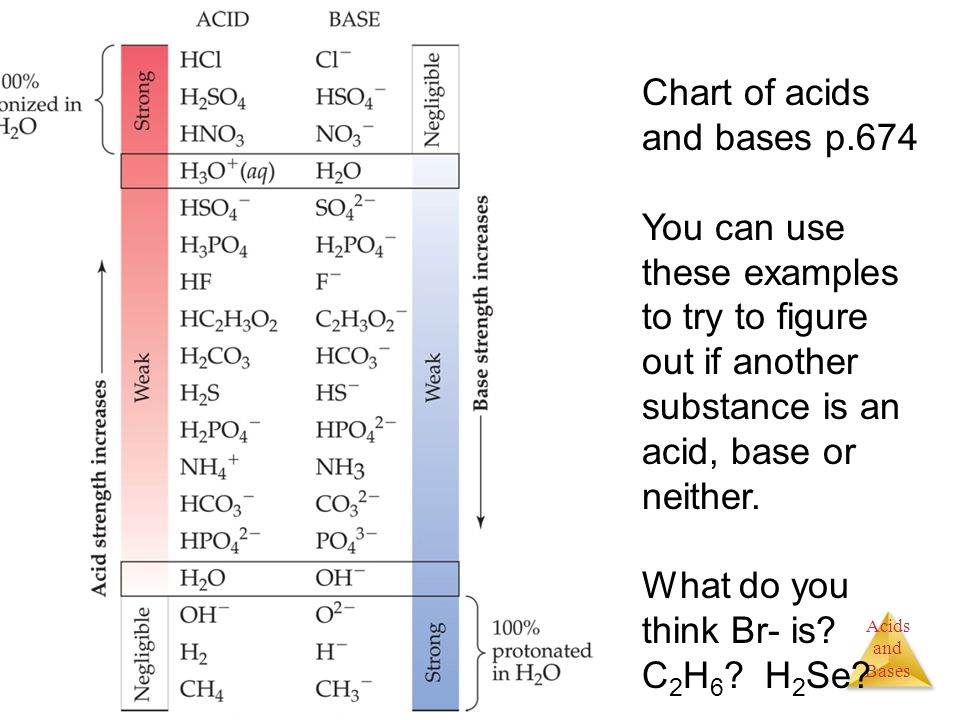
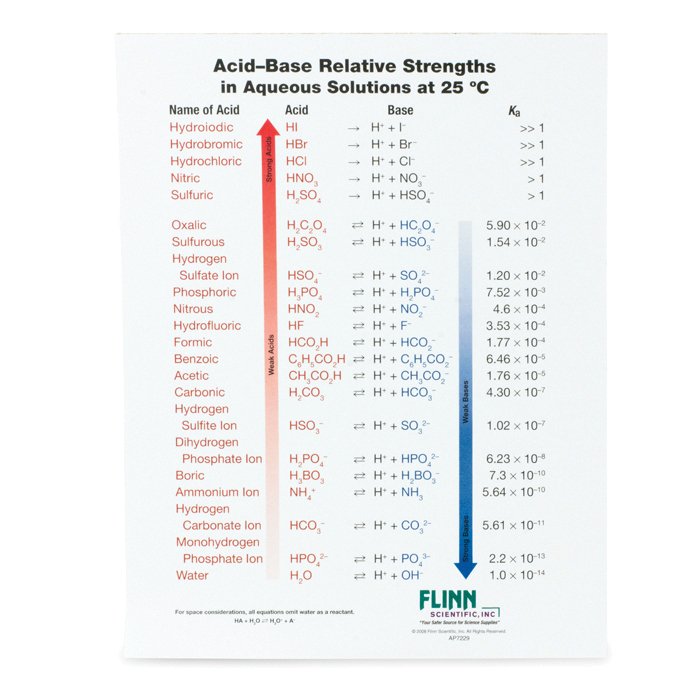
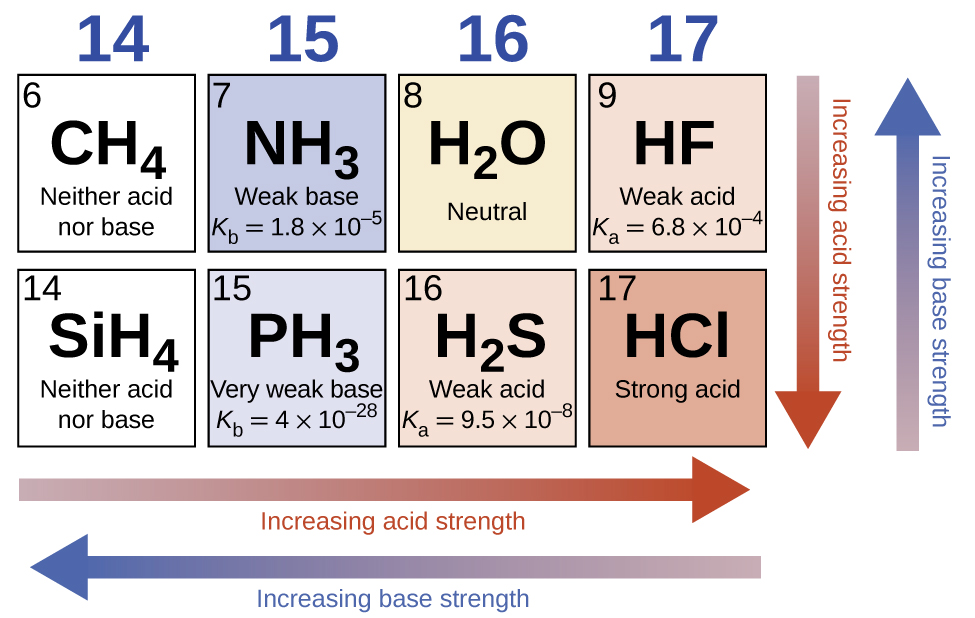
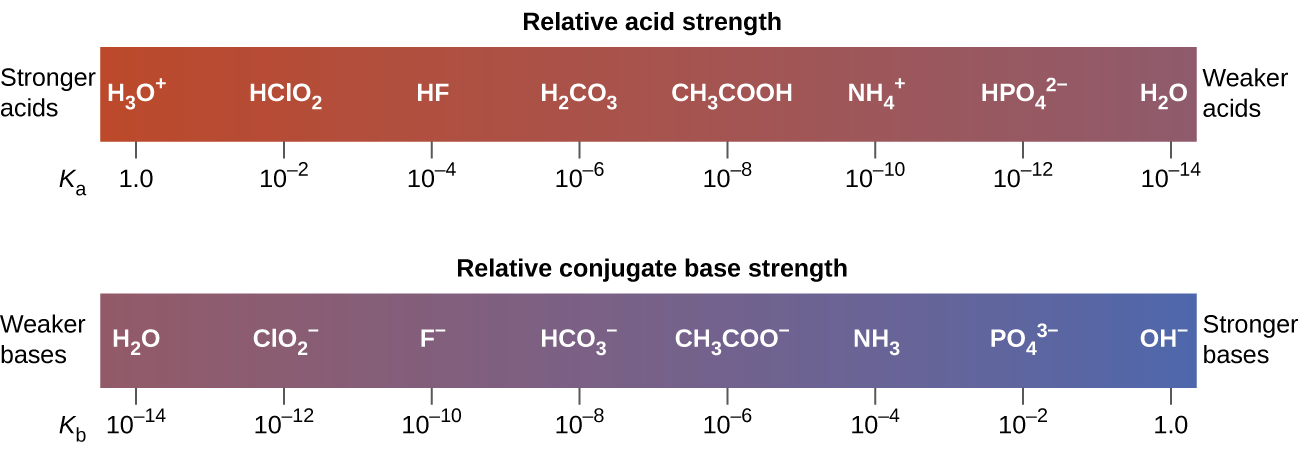
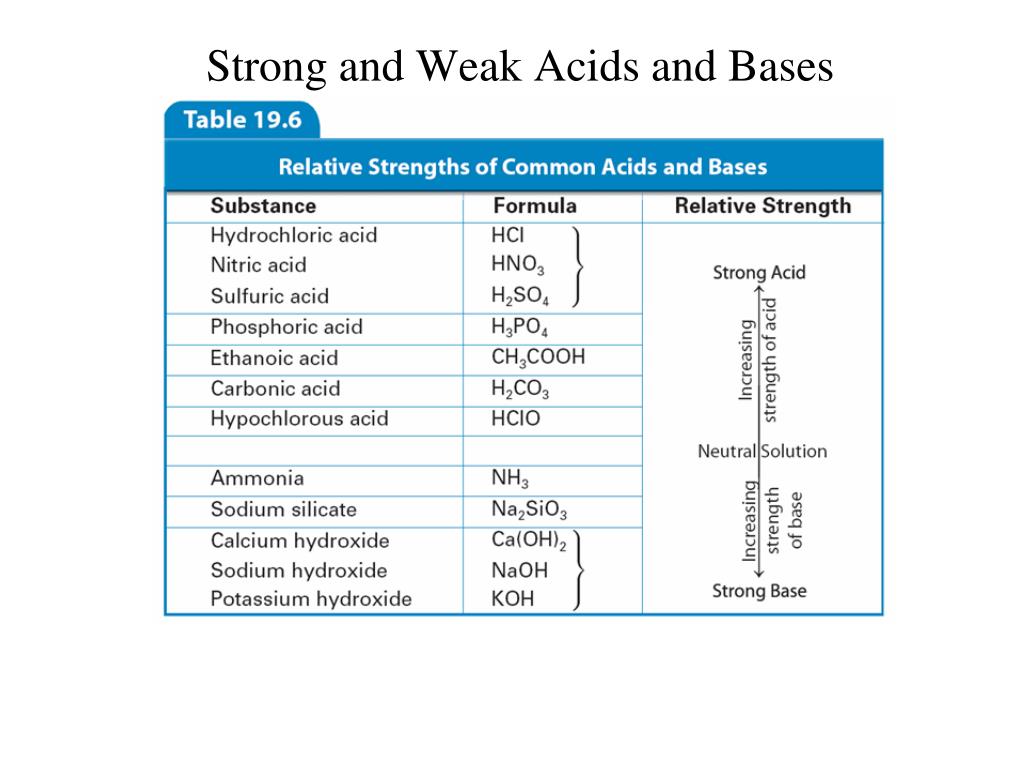
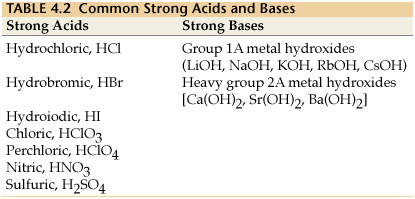
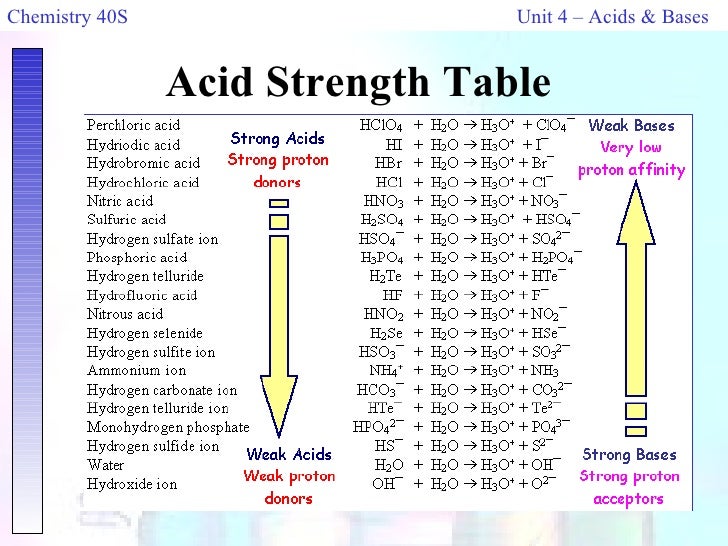
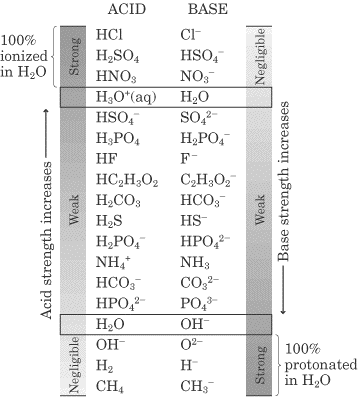
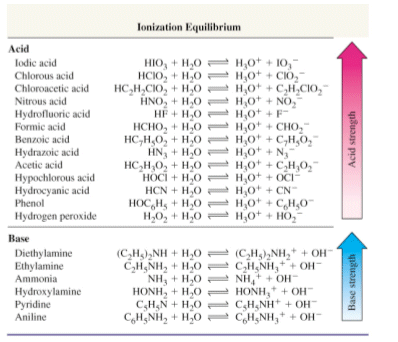
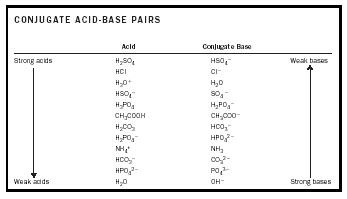
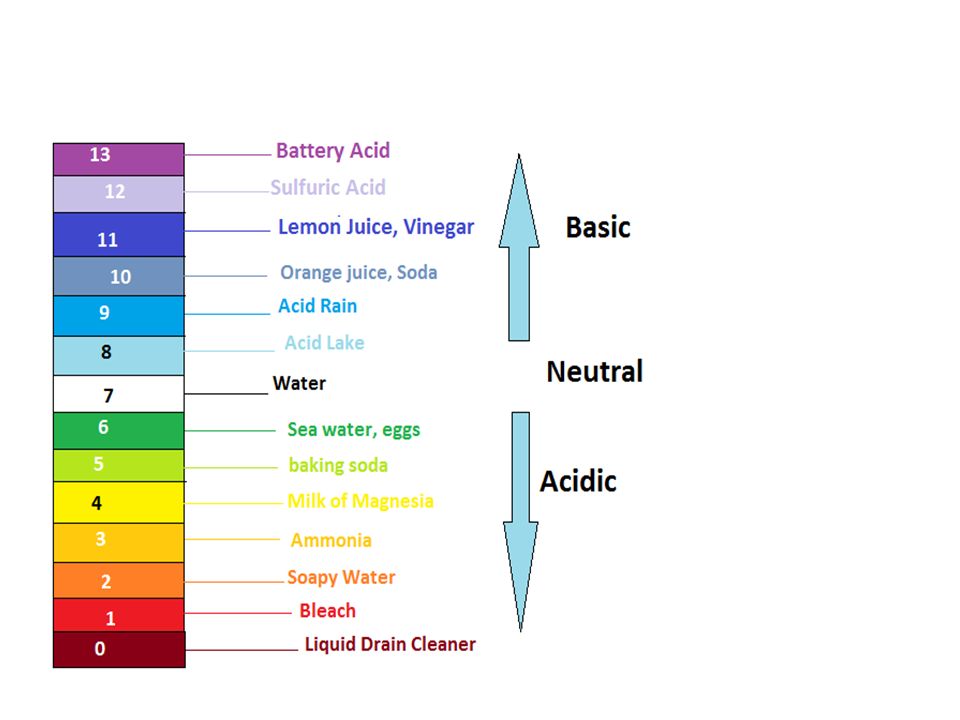
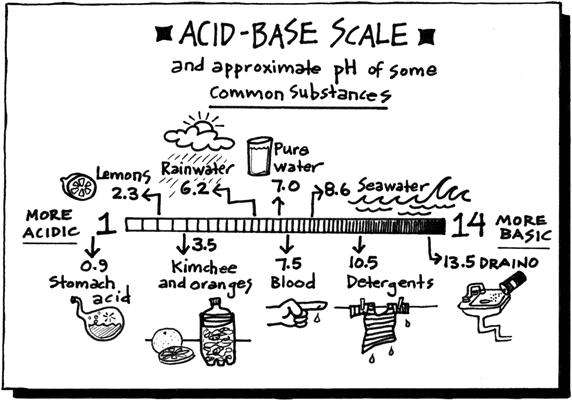
Acids and base chart. Bases are the chemical opposite of acids. The undissociated form of the indicator is a different color than the iogenic form of the indicator. Strong acids are listed at the top left hand corner of the table and have ka values 1 2.
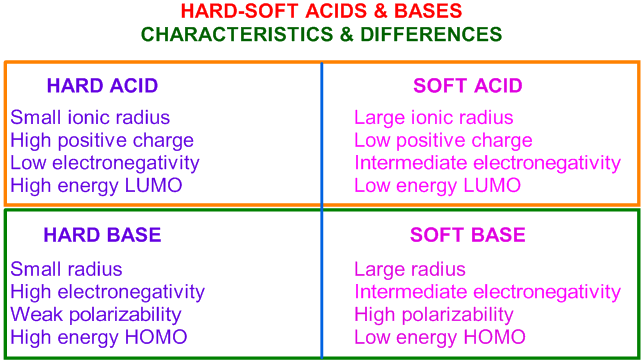
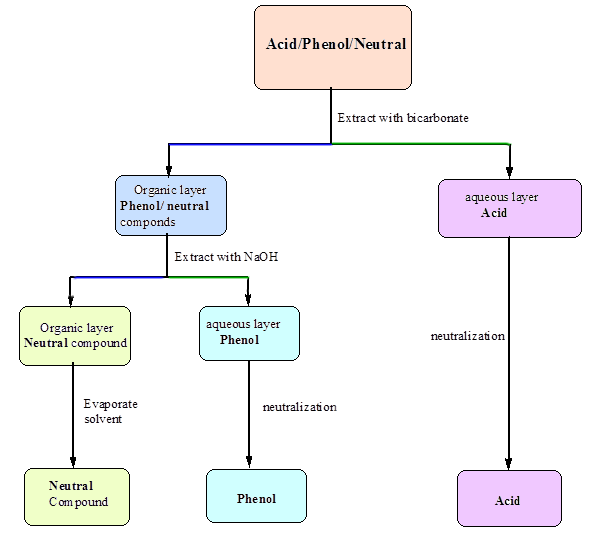
Some examples of hard and soft acids and bases are given in table pageindex 1. Chemical elements periodic table. When a base is dissolved.
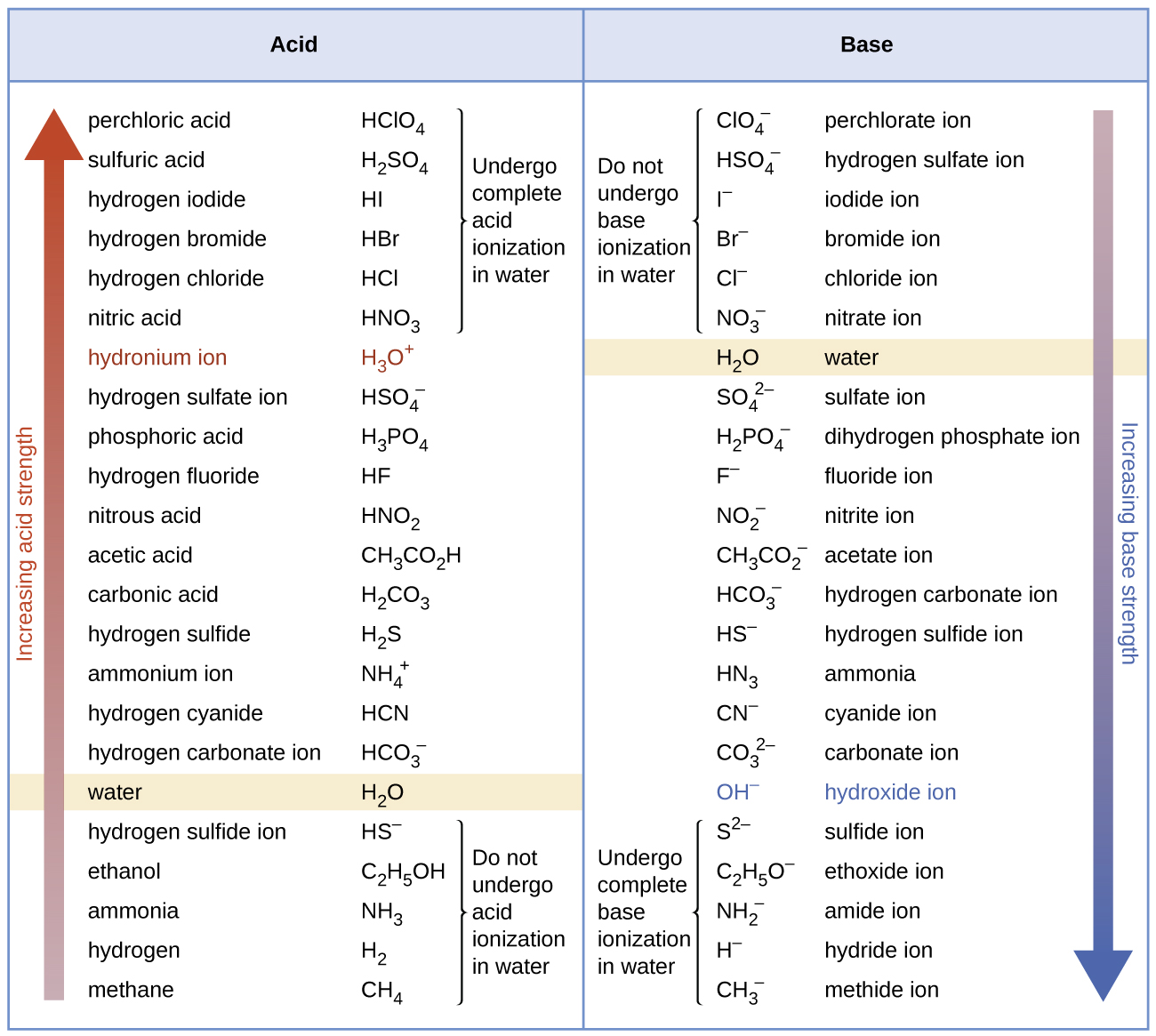
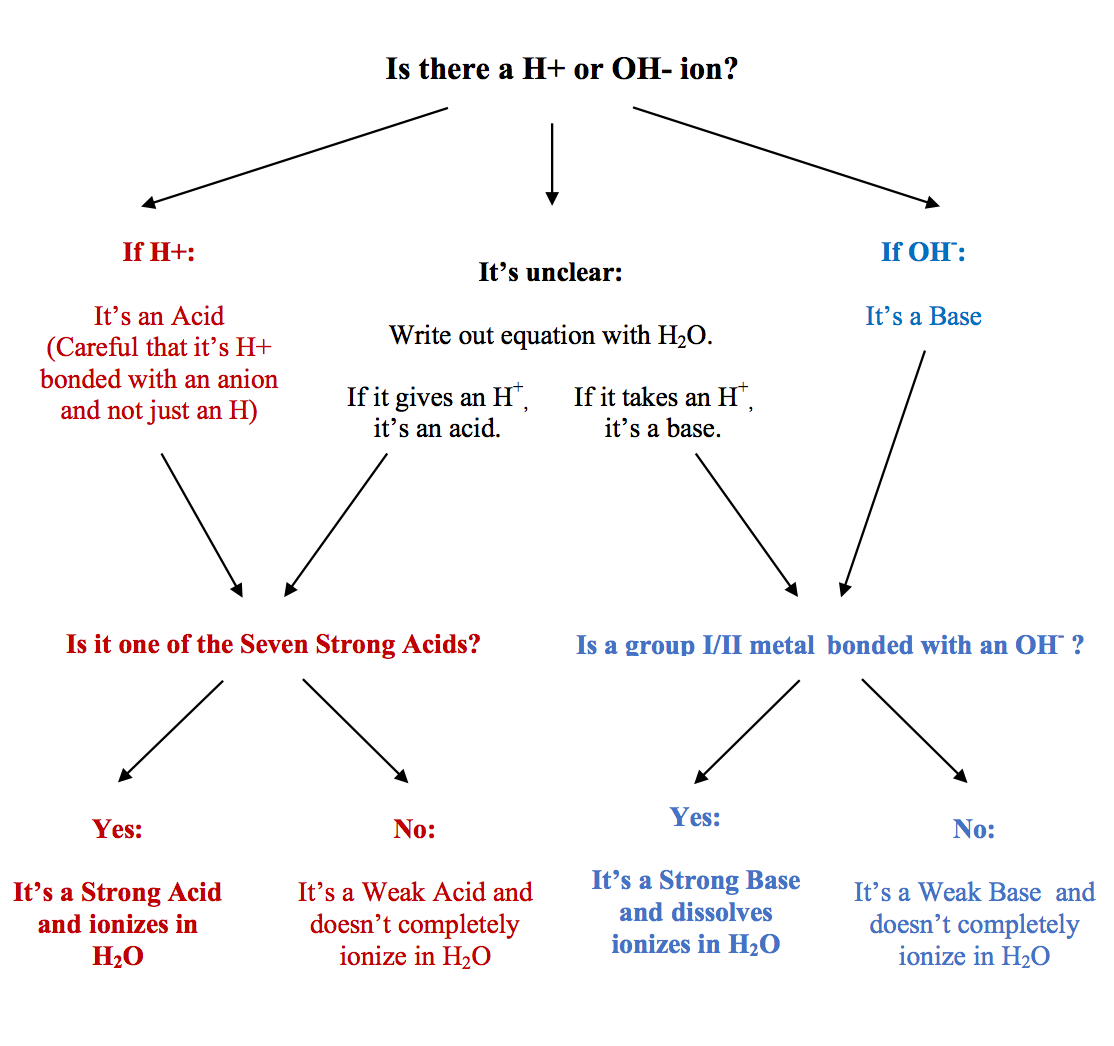
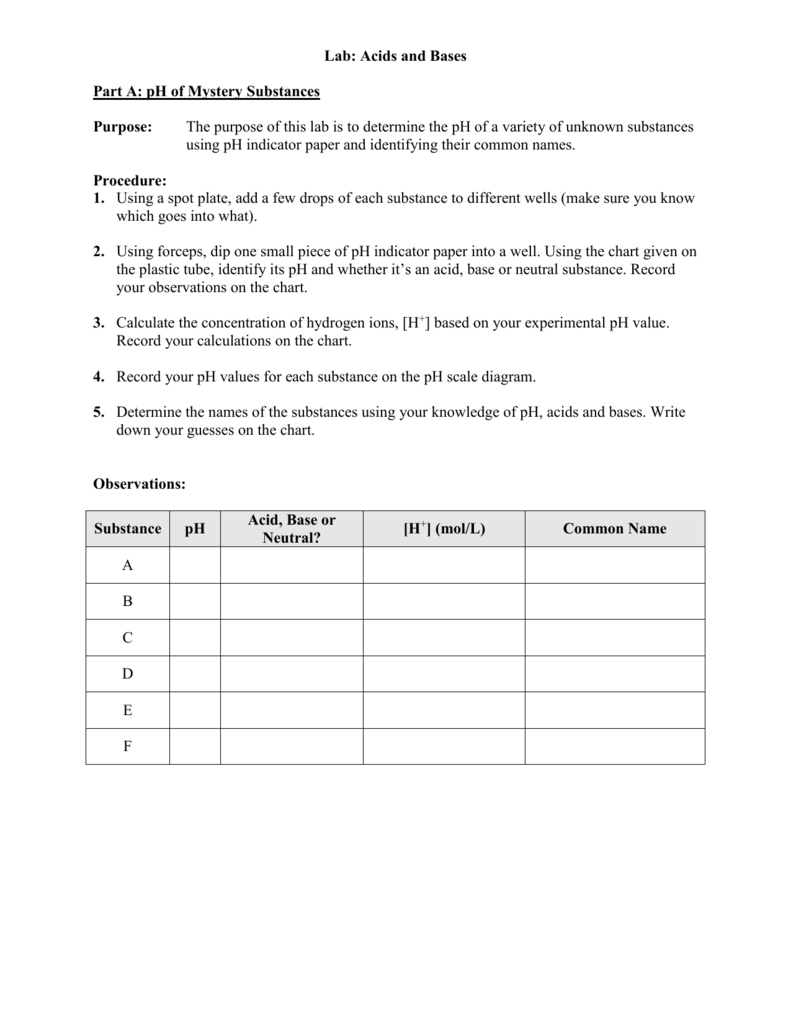
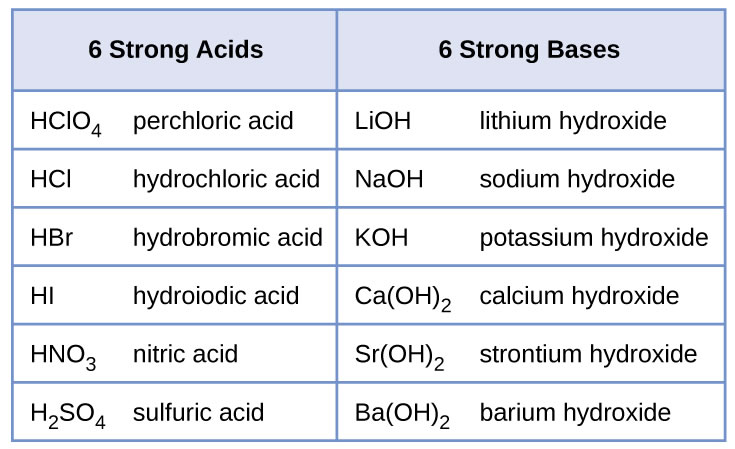
The strong bases are listed at the bottom right of the table and get. Find name molecular formula strength and reagent volume for your dilution. An acid is a substance that donates hydrogen ions.
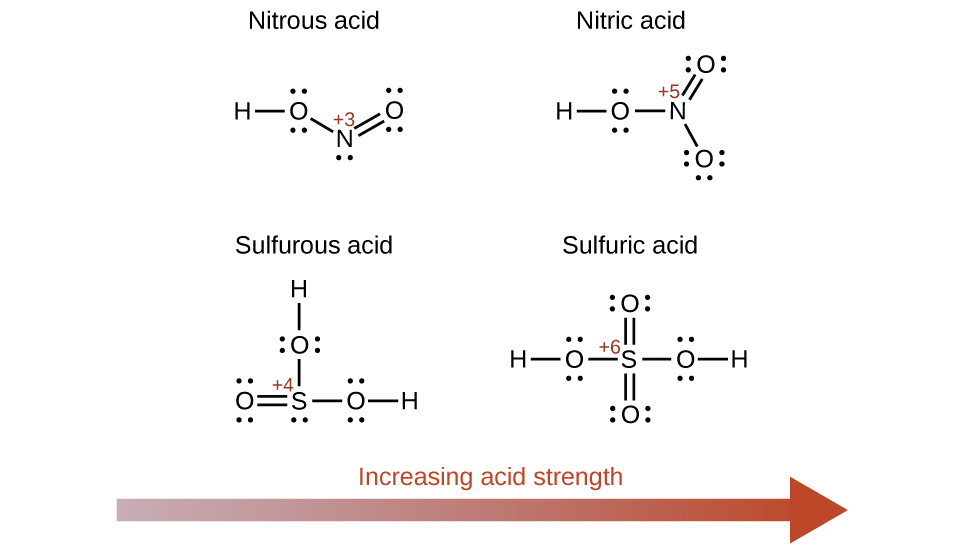
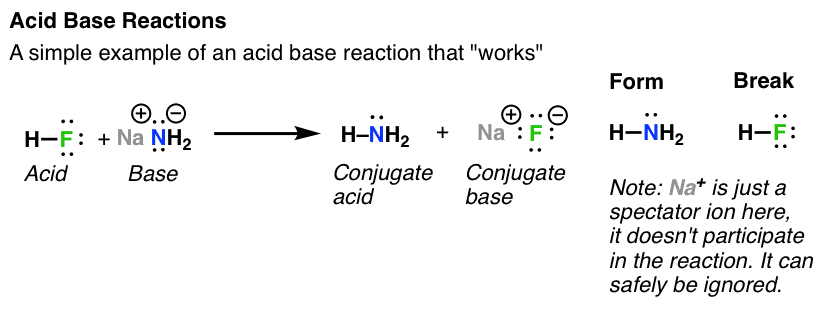
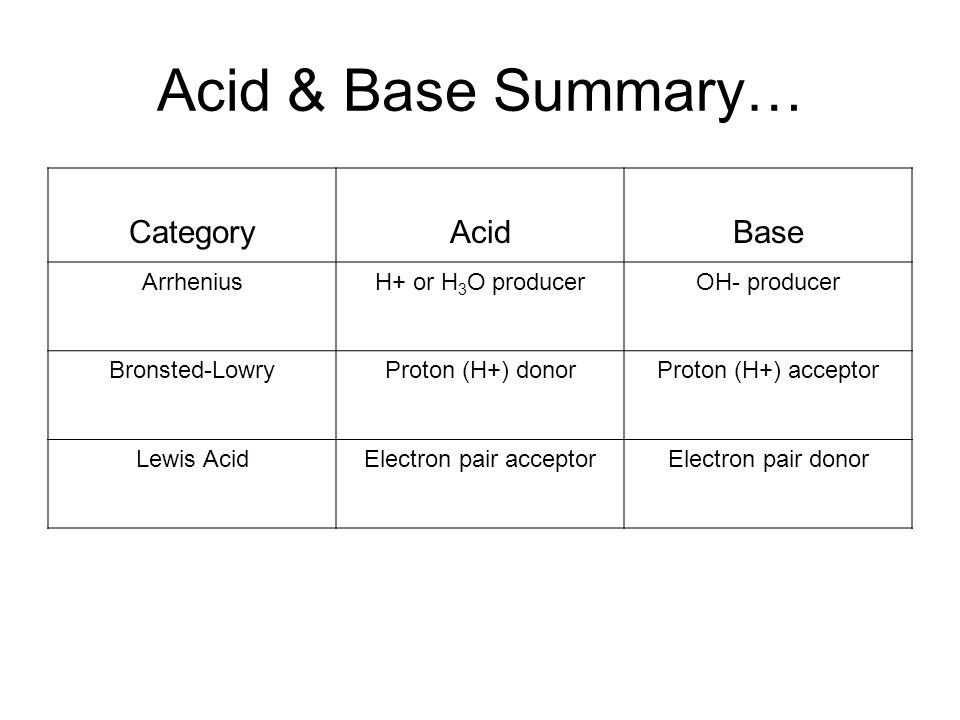
Acids and bases are one of the most important parts of chemistry but also play their significant role in another field of science. There are many definitions which differentiate the substances as acid and base but the most accepted are the arrhenius theory bronsted lowry theory and the lewis theory of acid base. Bh 3 ch 3 2 s h 3 b s ch 3 2 cao co 2 caco 3 becl 2 2 cl becl 42.
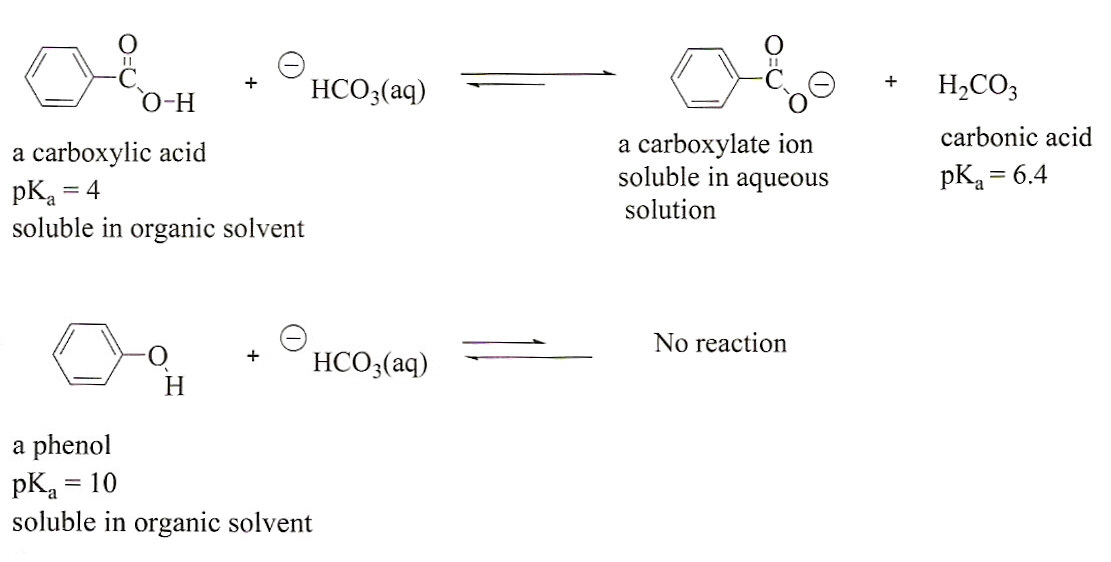
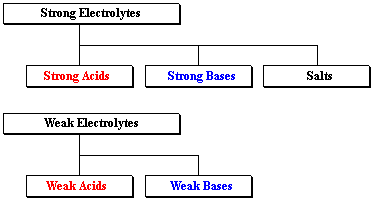
Metal ions with the highest affinities for hard bases are hard acids whereas metal ions with the highest affinity for soft bases are soft acids. This kind of solution is acidic. Our common acids and bases concentration reference chart allows you to easily prepare chemicals in a 1 normal solution.
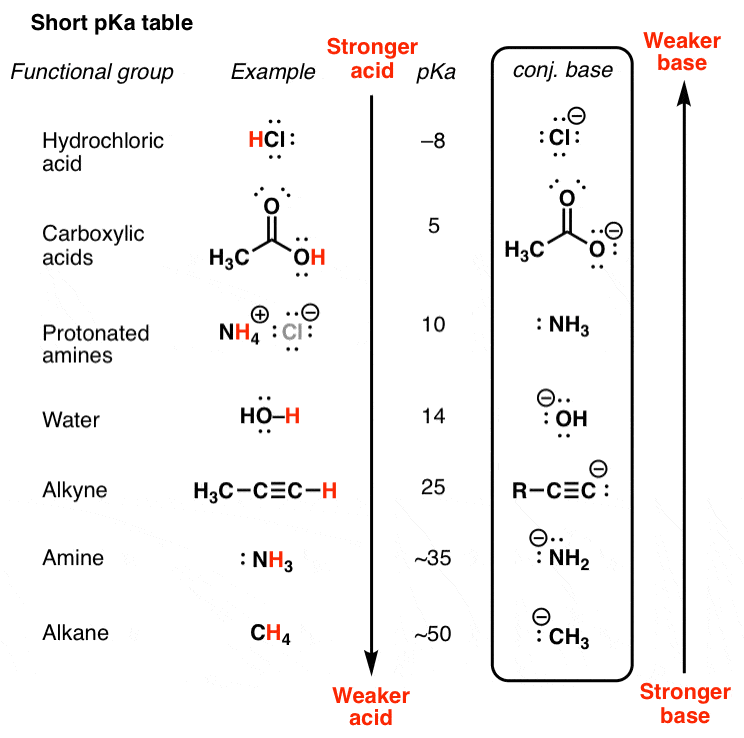
Acid with values less than one are considered weak. List of common organic acids. Because of this when an acid is dissolved in water the balance between hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions is shifted.
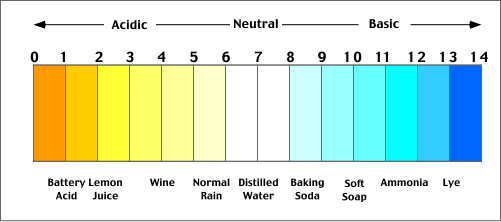
The strong bases are listed at the bottom right of the table and get weaker as we move to the top of the table. Acids are defined as compounds that donate a hydrogen ion h to another compound called a base traditionally an acid from the latin acidus or acere meaning sour was any chemical compound that when dissolved in water gives a solution with a hydrogen ion activity greater than in pure water i e. Now there are more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions in the solution.
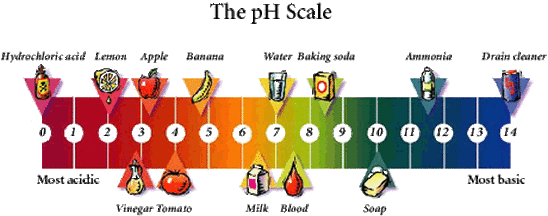
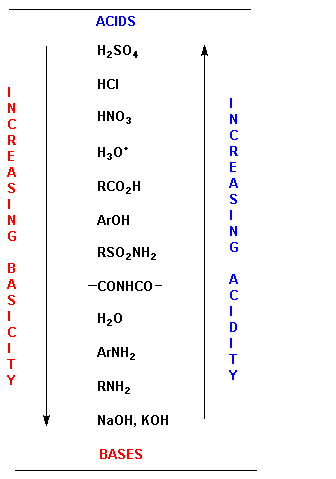
Complete list of bases. A ph less than 7 0. An indicator does not change color from pure acid to pure alkaline at specific hydrogen ion concentration but rather color change occurs over a range of hydrogen ion concentrations.































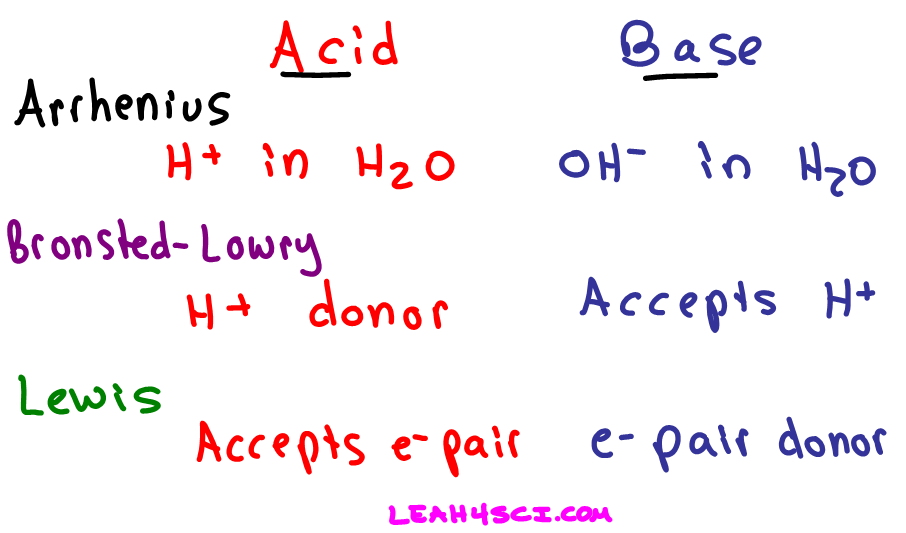


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/list-of-strong-and-weak-acids-603642-v2copy2-5b47abd0c9e77c001a395e55.png)









/GettyImages-680790165-5897802f3df78caebcf554a0.jpg)