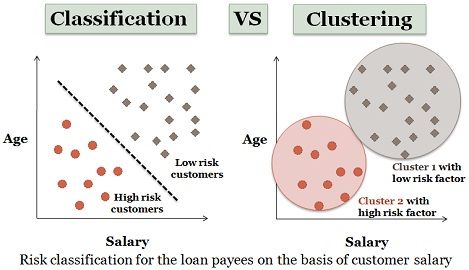
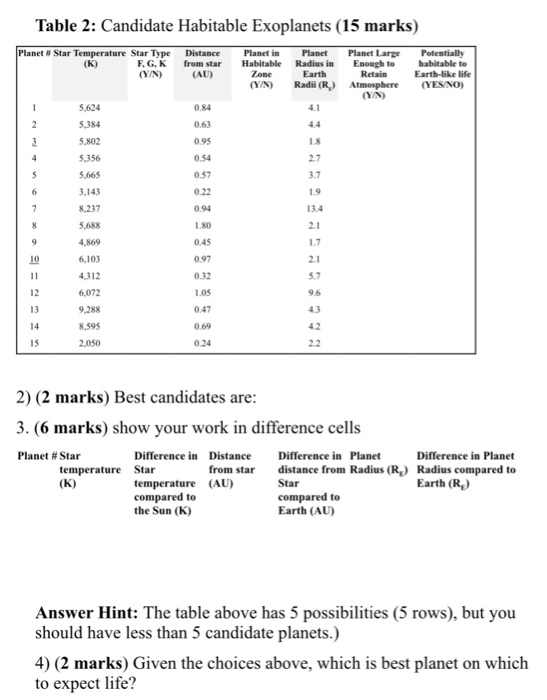
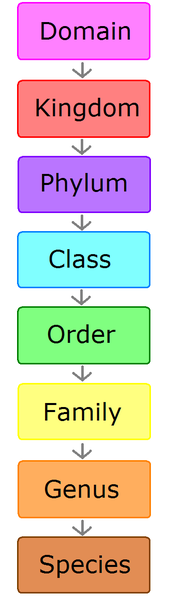
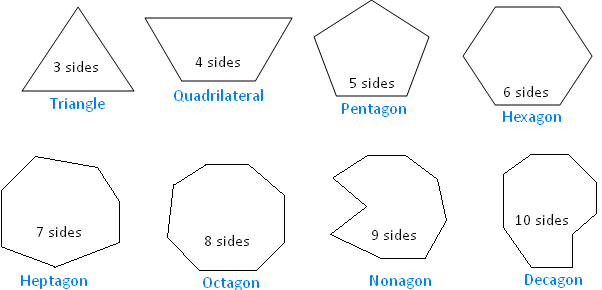
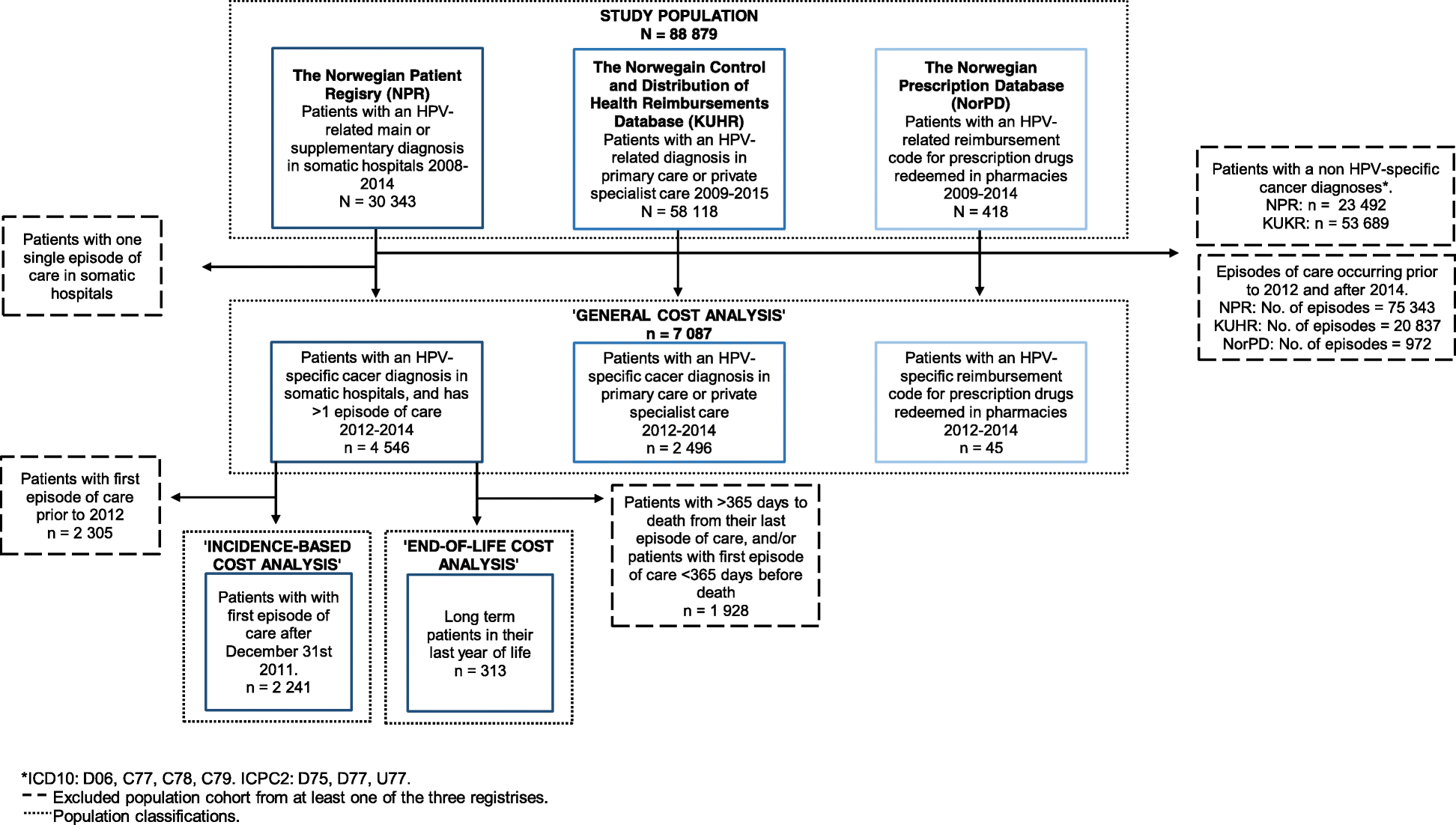
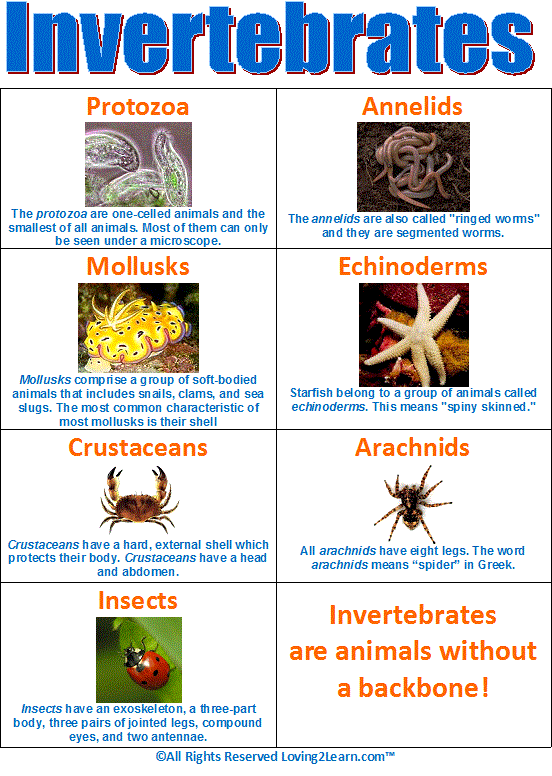
Classification Of Life Chart

This alternative scheme is presented below and is used in the major.
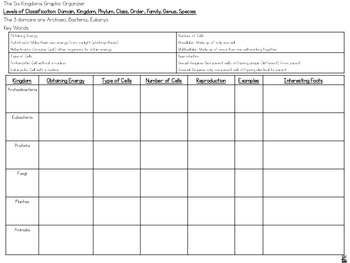
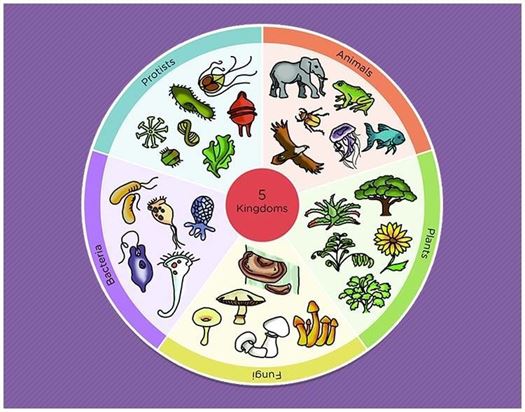
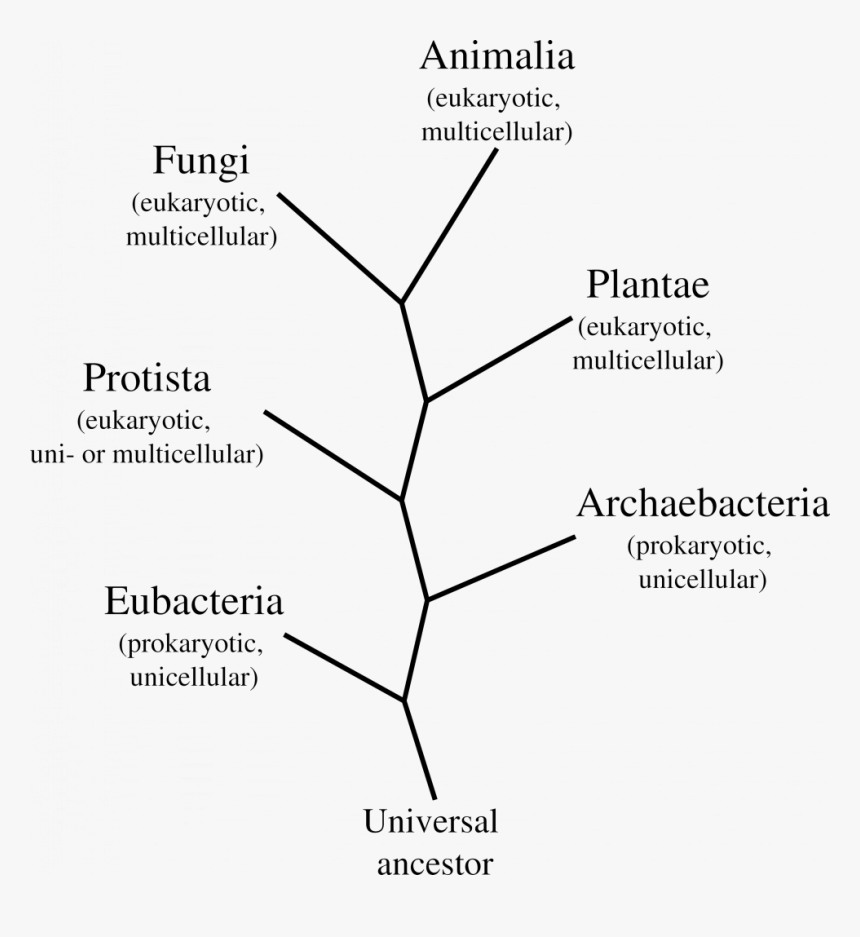
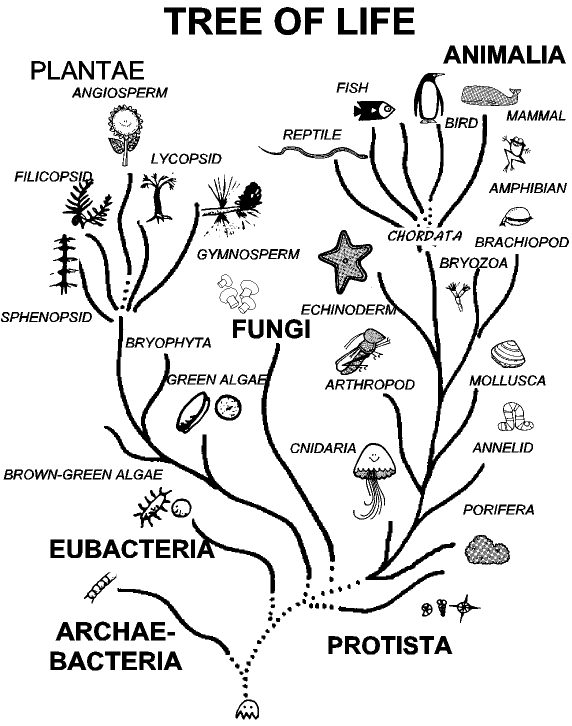
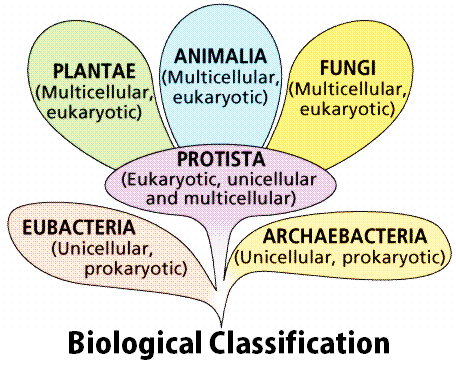
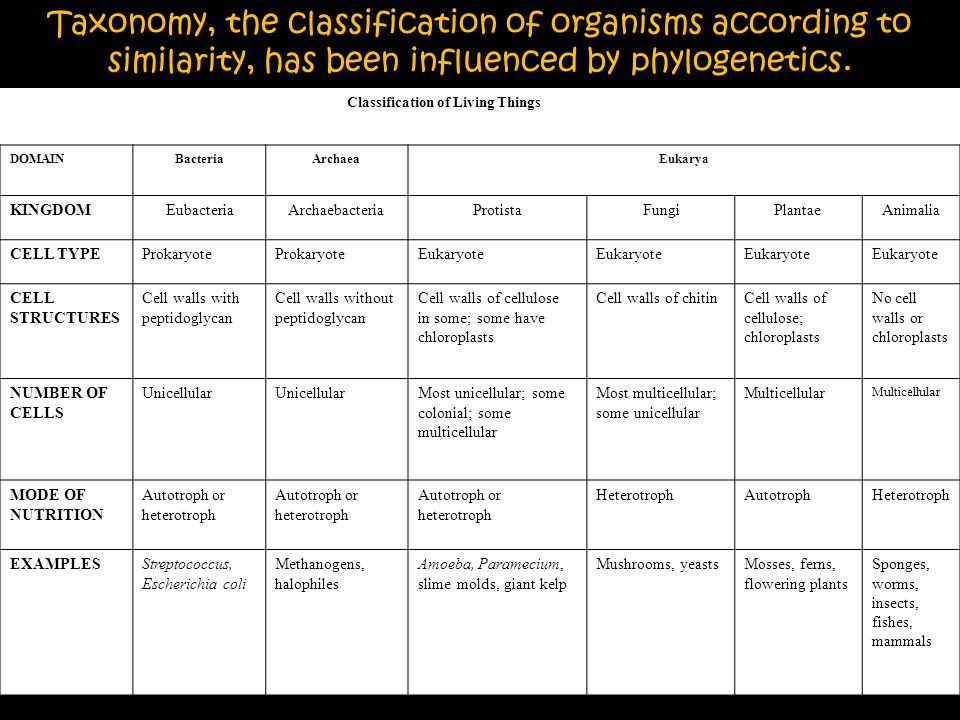
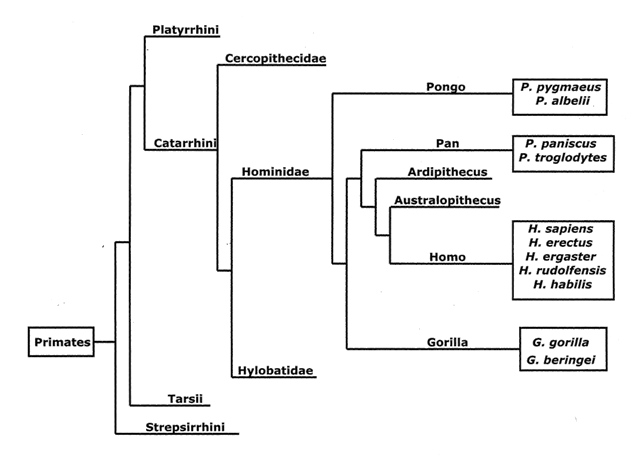
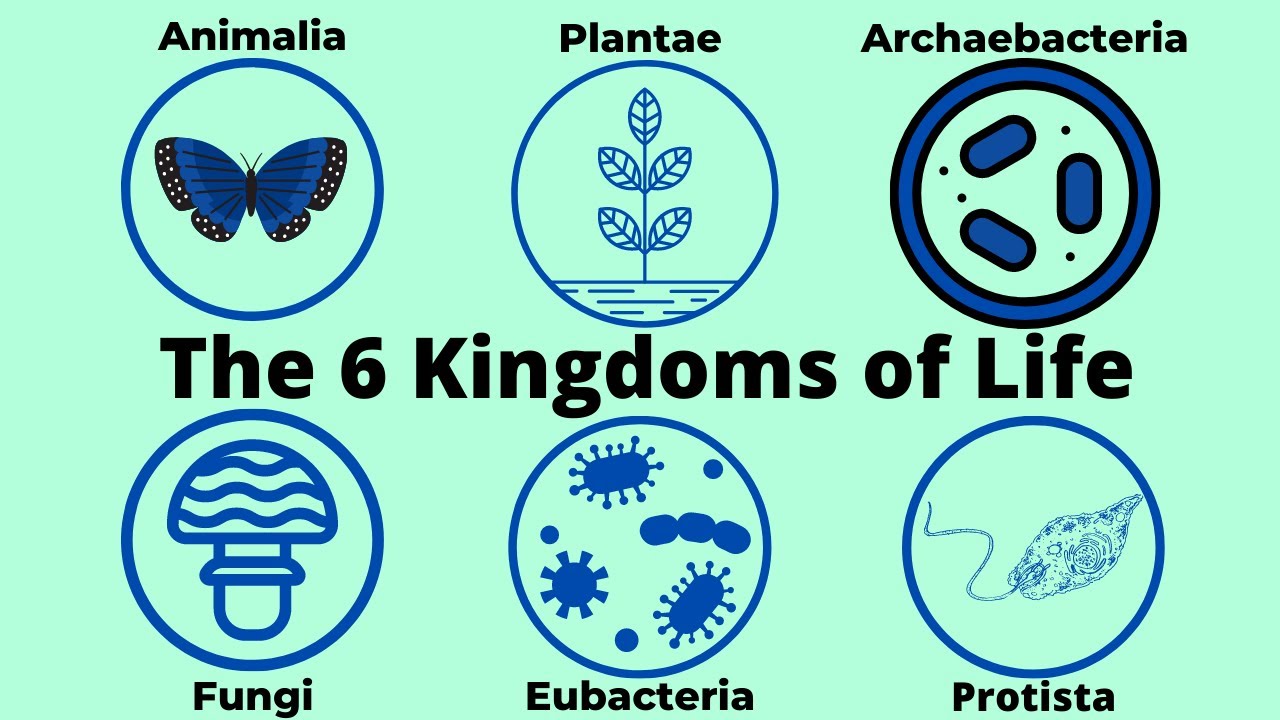
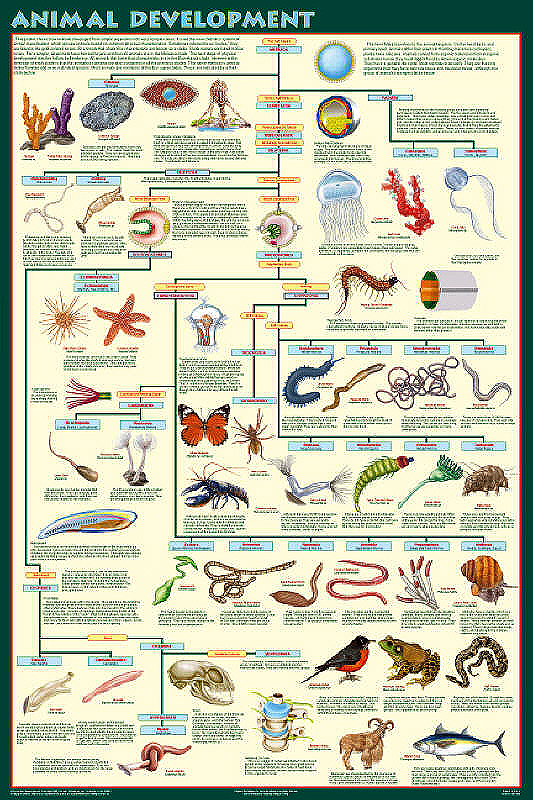
Classification of life chart. Recent advances in biochemical and electron microscopic techniques as well as in testing that investigates the genetic relatedness among species have redefined previously established taxonomic relationships and have fortified support for a five kingdom classification of living organisms. Over 250 plant animal and microbe species are arranged according to the most up to date taxonomy domain kingdom phylum order family and genus in a beautiful easy to follow tree of life format. Recent examples are that of adl et al 2012 and 2019 which covers eukaryotes only with an emphasis on protists and ruggiero et al.
24 x 36 inches on sturdy cardstock description. The table specifies asset lives for property subject to depreciation under the general depreciation system provided in section 168 a of the irc or the alternative depreciation system provided in section 168 g. A classification of living organisms.
In general organisms are identified by their binomial name consisting of the genus and species names. Classification of living things naming organism. In science the practice of classifying organisms is called taxonomy taxis means arrangement and nomos mean method.
The following are some basic nomenclatural rules that apply to all three codes. The genus name is always capitalized whereas the species name is not. The macrs asset life table is derived from revenue procedure 87 56 1987 2 cb 674.
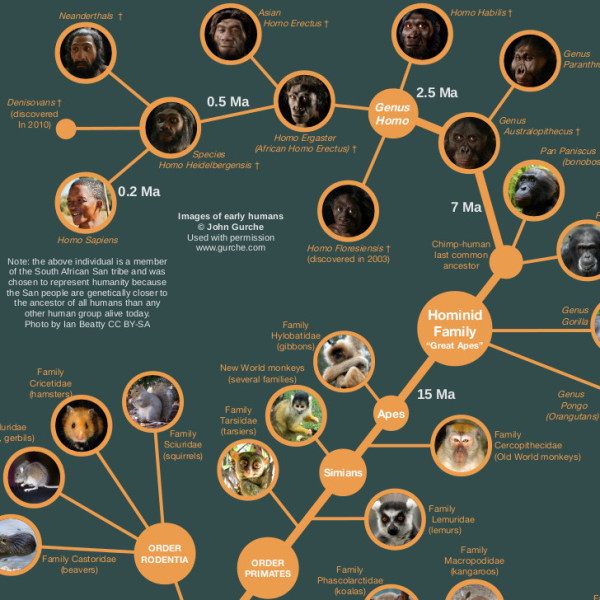
Based on a vintage design this chart shows how over 250 plants animals and microbes are classified into domains kingdoms phyla orders families and genera. This wallchart is unique in that it serves as both a timeline of evolution and a guide to biological classification. However comprehensive published treatments of most or all life are rarer.
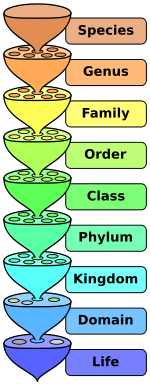
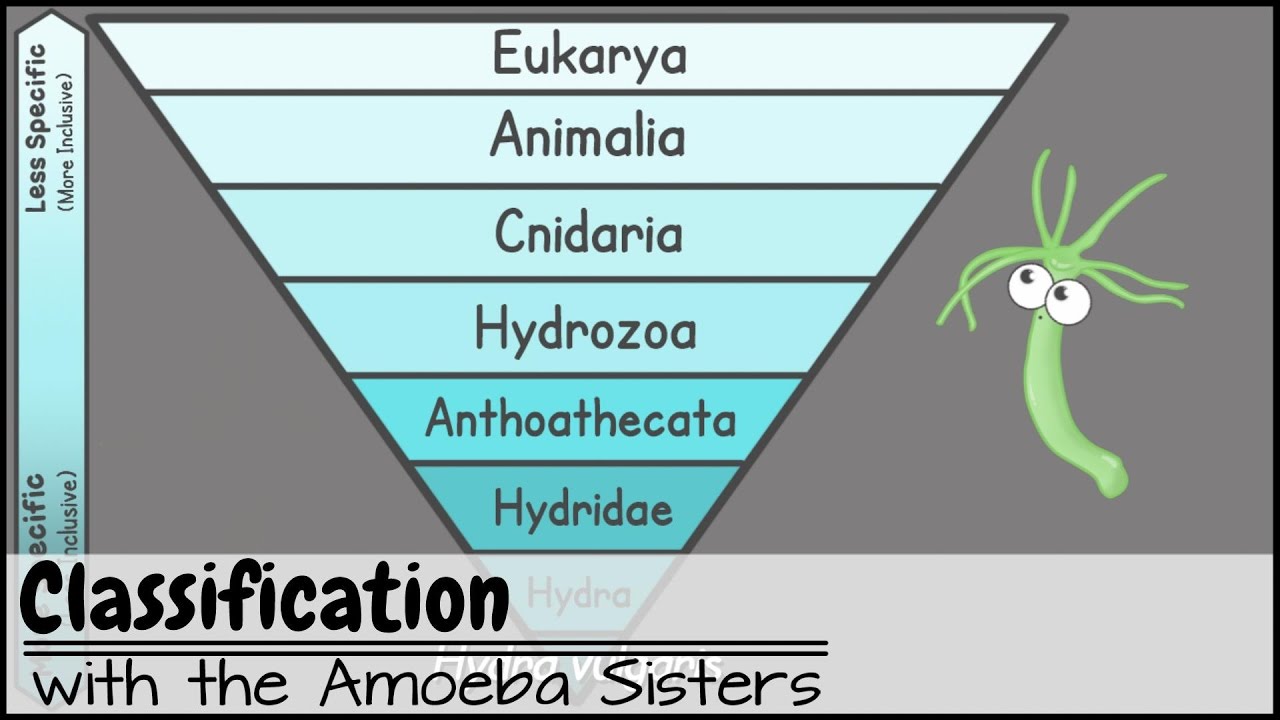
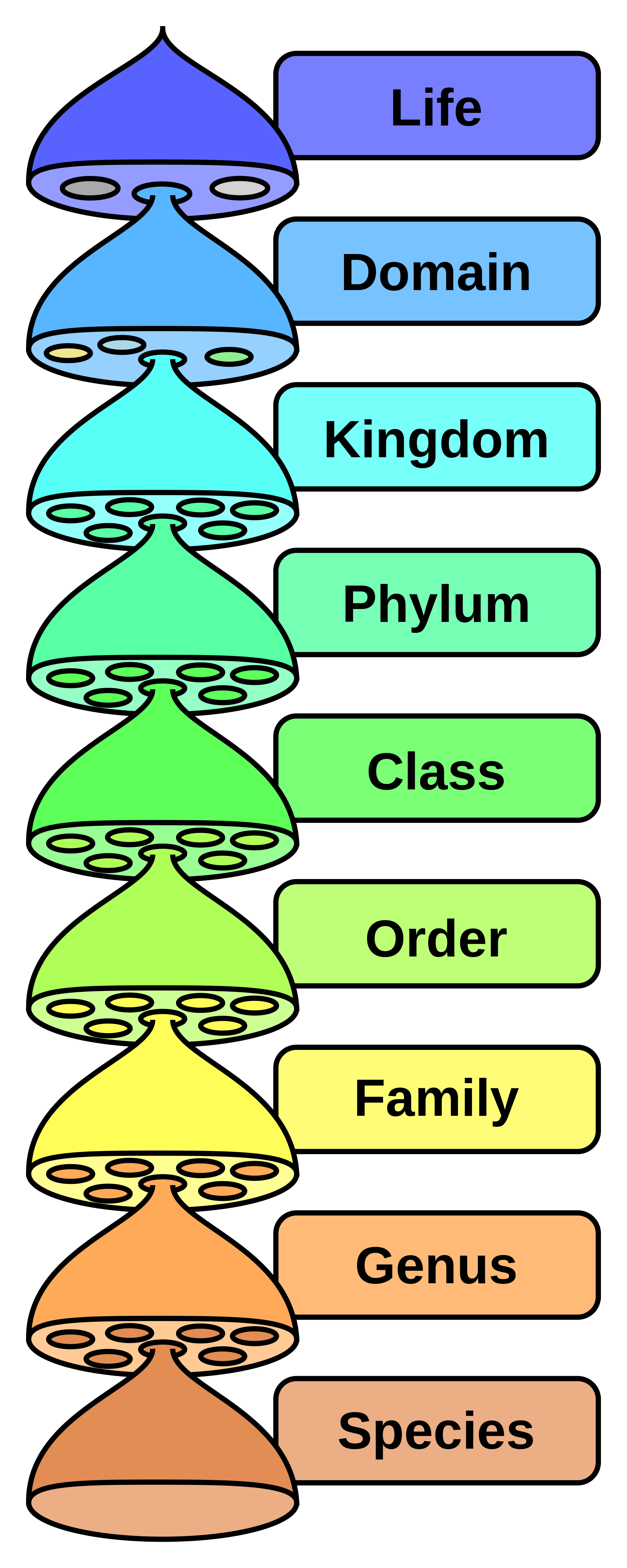
The classification of living things includes 7 levels. Both names are always italicized or. These specialized groups are collectively called the classification of living things.
The modern taxonomic system was developed by the swedish botanist carolus linnaeus 1707 1778. Partial classifications exist for many individual groups of organisms and are revised and replaced as new information becomes available. The chart focuses on species that are well known to the average person so that one can discover interesting things such as the fact that green peppers are closely related to petunias or that dolphins are closely related to barnyard animals.
This beautiful tree of life chart is both a timeline of evolution and a guide to biological classification domain kingdom phylum order family and genus. To remember these categories think.




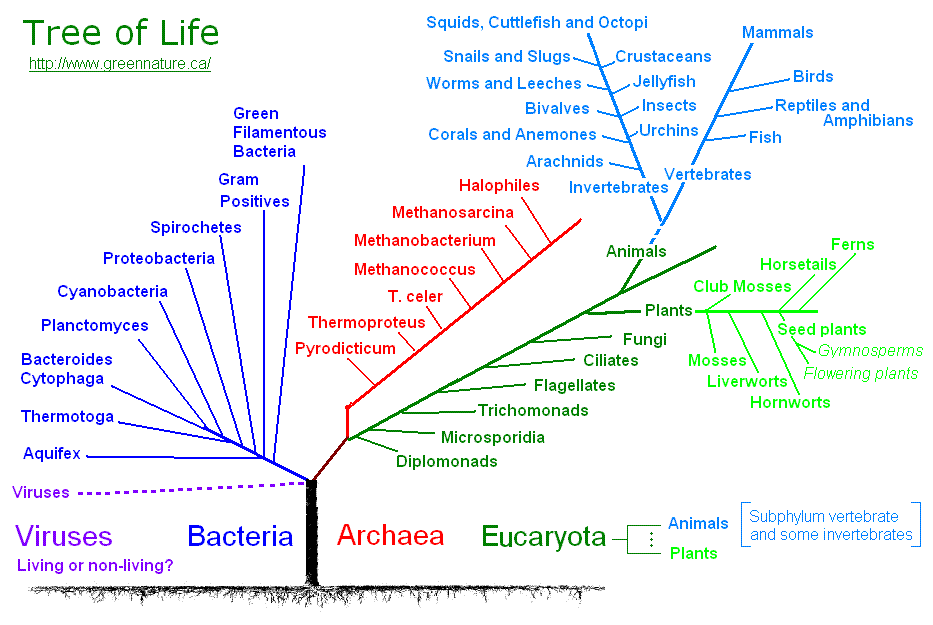



/six-kingdoms-of-life-373414-Final1-5c538e2446e0fb00013faa3c.png)



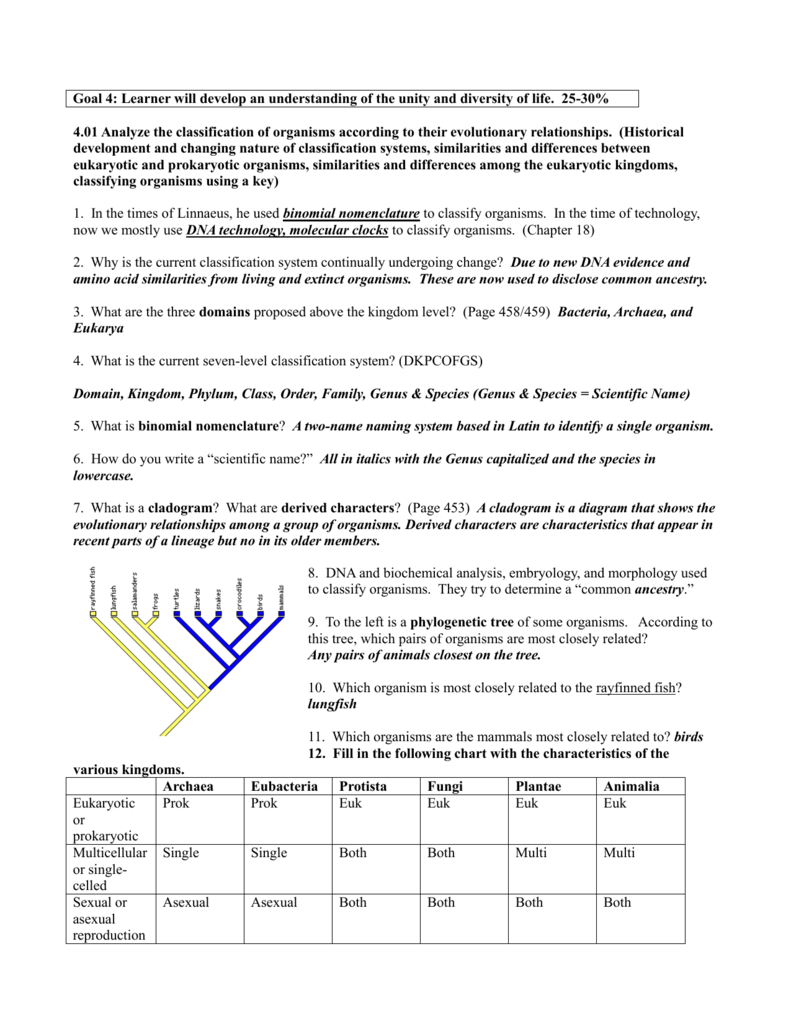

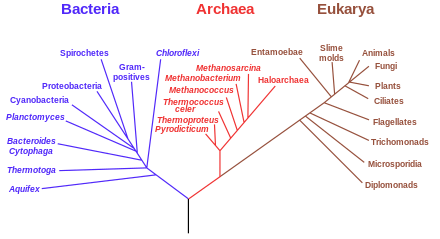





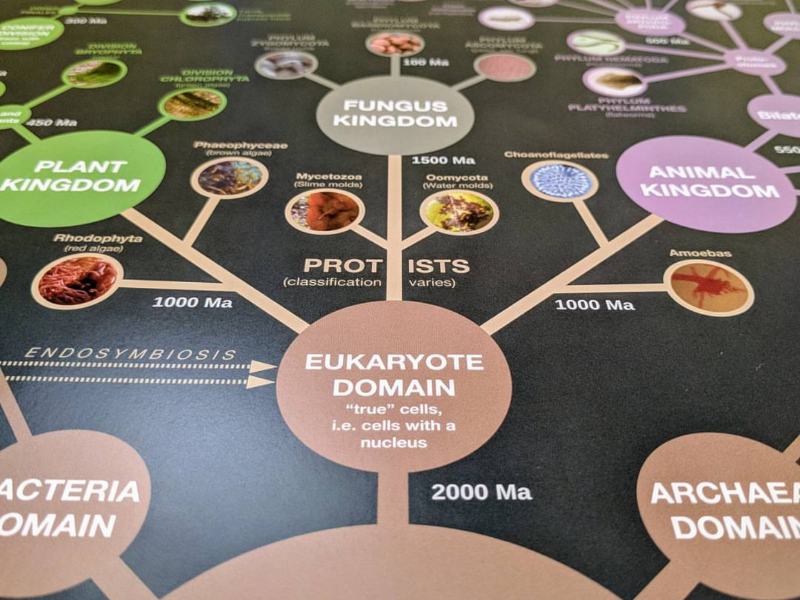
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/three_domain_system-57c48baa3df78cc16eb59931.jpg)